When you hear “blockchain,” you might instantly think of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. But there’s so much more to this technology than digital coins.
At its heart, blockchain is simply a smarter way to record, share, and secure information, without relying on a single middleman to keep everyone honest. And that has huge implications for businesses of all kinds.
If you’ve ever wondered how companies are actually using blockchain technology beyond crypto headlines, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll walk you through some of the most compelling real-world blockchain applications.
From tracking products across global supply chains to smart contracts and safeguarding healthcare records, you’ll see how blockchain is already reshaping the way organizations build trust and create value.
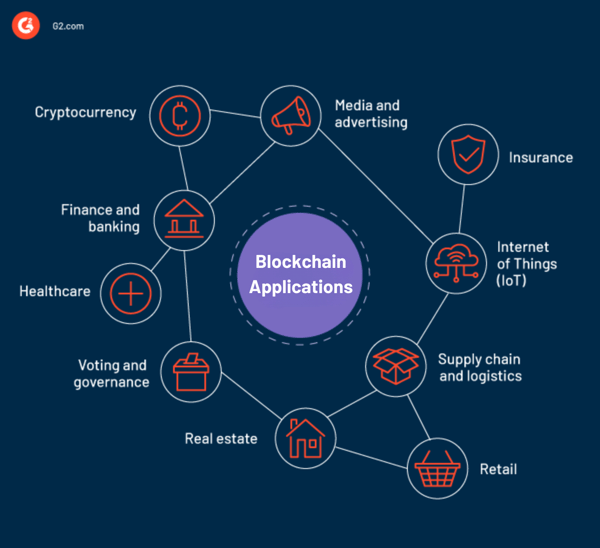
What are the top blockchain applications by industry?
| Industry | Key use cases |
| Healthcare | Secure EHRs, clinical trials, pharmaceutical supply chain, and patient monitoring |
| Finance and banking | Smart contracts, digital currencies, cross-border payments, and regulatory compliance |
| Real estate | Fractional ownership, mortgage security, land registry, and property management |
| Retail | Inventory management, supply chain transparency, and product authentication |
| Voting and governance | Tamper-proof voting systems, transparent governance records, and decentralized identity systems |
| Media and IP | Copyright protection, NFT-based ownership, piracy reduction |
| Energy and utilities | Peer-to-peer energy trading, grid data verification |
Businesses can build applications of blockchain for any purpose, like digital payments or supply chain, through blockchain platforms, often hosted by blockchain as a service providers. This distributed ledger technology (DLT) redefines how we operate in the digital economy by establishing trust and security for all.
TL;DR: Top blockchain applications at a glance
- What are the different blockchain applications? Blockchain applications and use cases go far beyond cryptocurrency, transforming industries like finance, healthcare, real estate, retail, and energy.
- How is blockchain used to protect healthcare data? In healthcare, blockchain secures electronic health records and tracks pharmaceutical supply chains.
- What are blockchain use cases in banking and finance? In finance, it powers smart contracts, digital currencies, and cross-border payments.
- How is blockchain used in real estate? Real estate benefits from tokenized property ownership and fraud-proof land registries.
- How do retailers use blockchain? Retailers use blockchain for supply chain transparency, product authentication, and customer data security.
- What are the future trends in blockchain? Future trends in blockchain include AI integration, green consensus protocols, cross-chain interoperability, and decentralized identity.
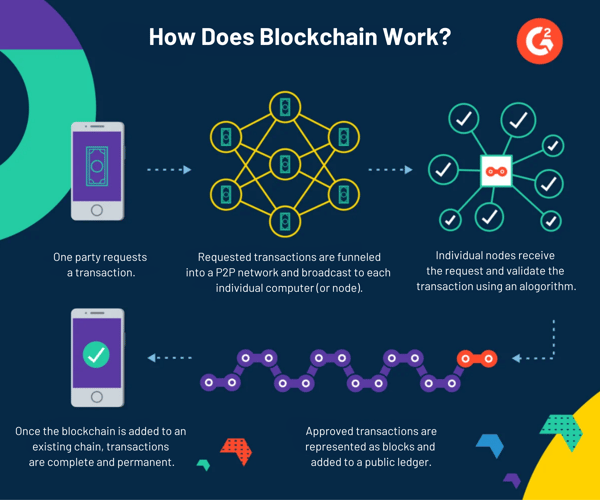
How does blockchain work?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger system that records and verifies transactions and information across a network of computers called nodes. Its core components comprise decentralization, transparency, immutability, and automation.
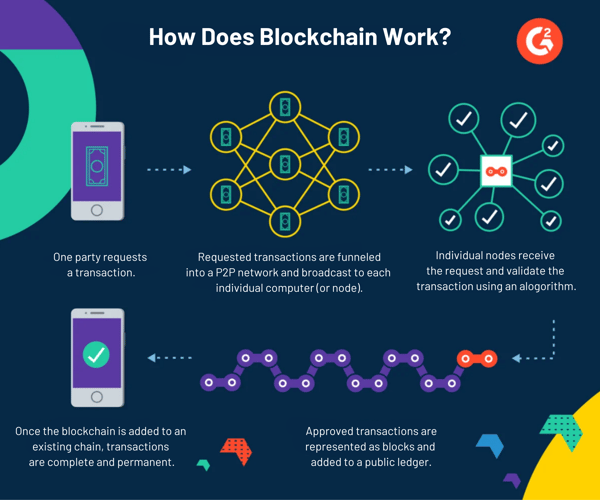
If we break down the term blockchain, we get block and chain. So to understand how it works, imagine a chain of blocks, where each block represents a data set. These blocks are connected in a distinct order to create a continuous chain.
Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain to ensure that the information is consistent and not controlled by a single commodity. This means that once a block is added to the chain, it’s difficult for any single entity to manipulate the stored data without alerting everyone in the blockchain network.
This secure data distribution is possible through a hash, which is generated from a cryptographic hashing algorithm. Hash is a digital fingerprint unique to each block and ensures that any slight change in the block’s data would result in a completely different hash.
Furthermore, to add a new block to the blockchain, its authenticity has to be validated via consensus. Consensus is a mechanism that ensures there are no discrepancies in the state of the distributed ledger. It’s essential in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. Once consensus validates the block, it’s added permanently to the blockchain. This action is then distributed across all nodes to update their copies.
Now that we’re clear on how blockchain works, let’s dive deep into some of the applications of blockchain technology across different industries and sectors.
Blockchain applications in healthcare
By embracing blockchain solutions, healthcare providers can modernize operations, maintain data integrity, and enhance patient care. Blockchain doesn’t encounter privacy breaches like traditional methods, where the risk of unauthorized access exists. It also enables secure data interoperability in real time, reducing administrative inefficiencies.
Here’s a look into what blockchain applications in healthcare comprise.
1. Secure electronic health records (EHRs)
Medical professionals can’t access complete patient history when patient data gets siloed. To overcome this problem, a blockchain-based system is linked to existing EHR software. The decentralized system stores and manages EHRs securely and provides a single view of a patient’s record. It also gives patients the freedom to approve changes to their EHRs, authorize who can view them, and control how they are shared by healthcare providers.
2. Clinical trial research
Clinical trials and continuous medical research are part of what takes a healthcare system to the next level. However, such initiatives are often burdened with data integrity issues. The blockchain serves as the single source of truth for research and trial data. It improves and secures record keeping and sharing while maintaining patient privacy.
Blockchain also asserts ethical checkpoints to ensure the trial is completed while staying compliant.
3. Pharmaceutical supply chain management
One of the persistent challenges in the healthcare industry is confirming the authenticity of medicines and pharmaceutical products. Blockchain offers visibility into each stage of the supply chain, enabling complete visibility and traceability of medical goods.
In a sector where counterfeit products cause thousands of deaths every year, the implementation of blockchain is one of the most secure and legit solutions to prevent such circumstances.
4. Verification of staff credentials
Similar to blockchain applications in supply chain management, the technology can track the records and credentials of medical professionals to streamline hiring processes. Trusted medical records with staff credentials are accessible to other healthcare organizations as needed. This practice enforces transparency when sharing staff details with patients.
5. Remote patient monitoring
Patient monitoring solutions have created one of the biggest shifts in the medical world. Healthcare practitioners are using advanced sensors to measure patients’ vital signs to provide enhanced preventative and proactive care remotely.
Blockchain supports it by providing encrypted communication and securing such devices from cyberattacks tampering with personal data.
Blockchain applications in finance and banking
Blockchain technology lies at the heart of the digital transformation in banking. It has evolved from crypto to securing loans, digital transactions, and online payments. It has become one of the most widely used technologies in fintech. Blockchain in banking and financial services enables efficient processes, reduced costs, and secure networks.
Check out some of the most common blockchain applications in finance and banking.
6. Smart contracts
Smart contracts software is built on blockchain-based platforms that automate the execution of agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries. They permit trusted transactions and agreements between two parties without a central authority. Smart contracts have several uses, including real estate, trading, healthcare, supply chain, and dispute resolution.
7. Digital currencies
With blockchain enabling and normalizing the use of digital currencies, financial trading, and transactions are much faster and more secure than ever. It has also paved the way for the development of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Furthermore, this new and efficient framework of digital assets exchange has opened the possibility of digital currencies becoming standard in the future.
8. Cross-border payments
By providing real-time tracking and secure payment gateways, blockchain has made cross-border payments faster, safer, and highly cost-effective. By reducing the element of a middleman and transaction fees, blockchain has enabled banks and customers to transact more frequently.
9. Regulatory compliance
Blockchain provides transparent and auditable records of digital transactions, which helps financial institutions meet regulatory requirements. Banks can also intercept suspicious transactions and digital banking activities on time by streamlining the auditing process with blockchain technology.
10. Asset management
There are many ways through which blockchain solutions make asset management more advanced. It digitizes the portfolio and existing holdings for wider market access, liquidity, and ease of transfer. Blockchain also improves investor and stakeholder governance through customizable, built-in privacy settings.
Blockchain applications in real estate
Businesses and professionals are becoming increasingly cognizant of blockchain applications in the real estate sector. It can transform property management and sales, optimize payments, and increase investment opportunities.
Here’s a look at the different uses of blockchain in real estate.
11. Fractional ownership and asset tokenization
Through blockchain, the process of real estate investment is repurposed, allowing investors to buy and sell fractional shares instead of pooling all their money to acquire property. Asset tokenization platforms built on blockchain let you create a digital token of ownership for real-world liquid assets. Once assets are tokenized, investors only need a trading app to execute borderless international trading.
12. Loan and mortgage security
Blockchain solves many challenges that come with paper documentation for loans and mortgages. Digitization of such documents provides access to critical information that supports future decisions like ownership rights and loan payment history.
Blockchain payment systems enable the use of smart contracts that automate the collection and distribution of payment along with real-time reporting.
13. Land registration
By letting go of the paper system, blockchain serves as the single resource in the form of an immutable ledger system. It tracks and updates any changes in the database, including land titles, boundaries, and land use planning. The digitization of such processes eliminates any excessive administrative costs and prevents fraudulent transactions.
14. Property management
Large-scale enterprises and startups often lack oversight of their portfolio. Blockchain in real estate secures data sharing and payment processes, providing effective due diligence across the global portfolio. It also simplifies all property management communication between owners, tenants, and service providers.
15. Urban planning
Any form of property development can’t happen without feedback from the community. However, people often feel deprived of the planning process or unable to express their preferences. Through blockchain, platforms can focus on providing educational resources and create an effective feedback loop between stakeholders to establish engagement and communication.
Blockchain applications in retail
In retail, blockchain acts as a tool for establishing trust between retailers, consumers, supply chain participants, and payment gateways. Blockchain’s ability to amplify the tracking and digitization of processes has been beneficial to the retail industry, especially during the pandemic.
Let’s break down the use of blockchain in retail below.
16. Inventory management
To improve overall efficiency, retailers need to be on top of their inventory management game. Blockchain makes this process more efficient by keeping track of the stock and expiration dates. It also automates the process of identifying product shortage or surplus, depending on consumer needs.
17. Supply chain management
By providing end-to-end visibility in the supply chain, blockchain allows all network participants to look into what’s happening in the system at any given time. It keeps track of everything throughout the product journey, addressing issues of supply chain discrepancies and lack of traceability.
18. Product authentication
Blockchain’s ability to verify product provenance has helped companies combat counterfeiting by identifying its proof of origin. By scanning blockchain-based radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, customers can extract details about the manufacturing process of a product, along with its ingredients and certifications.
19. Protection against cyber attacks
The issue of data privacy is common in every industry, and retail is no exception. Blockchain increases customer data security by storing encrypted data, which prevents unauthorized access or other cybersecurity breaches. This also benefits companies by gaining customer trust, which ultimately adds up to higher revenue.
20. Transparent product reviews
Another aspect of gaining customer trust is blockchain-based review systems. These systems are secured against unauthorized tampering and generate authentic reviews from customers. Trusted customer feedback builds credibility for the brand, resulting in increased customer loyalty and engagement.
Other applications of blockchain
Here are some more examples of blockchain applications across industries.
21. Voting and governance: Blockchain-based voting systems enhance the security and transparency of elections. Each vote is tamper-proof and auditable for easy verification and validation. Therefore, blockchain rids the system of voter fraud and any kind of data manipulation.
22. Intellectual property management: Blockchain supports the registration of intellectual property rights by making the process faster, more accurate, cost-effective, and secure. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are built on the Ethereum blockchain and add visibility of ownership and ease of trading for digital assets.
23. Energy trading: Blockchain technology combined with IoT devices enables consumers to trade and purchase energy directly from the grid rather than from retailers. It also provides an immutable record of meter readings, energy generation, and consumption data.
24. Insurance: With blockchain, insurance companies streamline all the processes, including claims processing, fraud detection, and underwriting. It also supports customer data protection by storing policy data in a tamper-proof ledger system, which improves accountability and trust.
25. Education: Educational institutions can verify candidate credentials and certifications through blockchain. They can access and share this data securely with authorized personnel, giving them full control. Also, blockchain can develop decentralized e-learning content software for securing educational content ownership.
26. Media and entertainment: While the media and entertainment industry is yet to utilize the full potential of blockchain, the technology helps artists and content creators get their dues, both in terms of revenue and copyrights. It also offers support for tackling piracy and fraud.
27. Gaming: Blockchain allows players to truly own in-game assets as NFTs, enabling trading and interoperability across different games. Examples of games using this technology include Axie Infinity and The Sandbox. Blockchain also supports “play-to-earn” models where players can earn cryptocurrency or NFTs.
What are the future trends in blockchain applications? (2025 and beyond)
Blockchain technology is moving well beyond cryptocurrencies. Here are the most important trends shaping where it’s headed next and why they matter for businesses exploring real-world applications:
AI integration for smarter workflows
Blockchain networks are increasingly combined with artificial intelligence to unlock new automation capabilities. For example, AI models can analyze transaction data to detect fraud patterns as they happen, while smart contracts can automatically adjust pricing or terms based on predictive insights. This convergence will make decentralized systems more intelligent and responsive.
Energy-efficient consensus models
Sustainability concerns have driven many organizations away from traditional Proof of Work systems, which consume massive amounts of electricity. As a result, more blockchains are adopting energy-saving protocols like proof of stake and delegated proof of stake. This shift not only reduces environmental impact but also lowers operational costs for enterprises.
Cross-chain interoperability
Right now, many blockchains operate as closed ecosystems. Emerging interoperability frameworks, such as Polkadot and Cosmos, make it possible for different networks to exchange data and assets securely. This will enable use cases like supply chains that span multiple blockchains or payments that move seamlessly across platforms.
Decentralized digital identity
Instead of relying on banks or governments to verify identity, blockchain can give individuals control over their credentials. A decentralized identity system lets users store verified identity information on a blockchain and share it selectively. This has big implications for streamlining onboarding, improving privacy, and reducing fraud.
Tokenization of physical and financial assets
Businesses are exploring how to represent tangible assets (like real estate, equipment, and inventory) and intangible ones (such as intellectual property or carbon credits) as digital tokens. Tokenization can simplify ownership transfers, speed up settlement times, and create new ways to raise capital.
Regulatory clarity driving adoption
Until recently, inconsistent regulations held back blockchain adoption in many industries. Now, governments are drafting clearer rules around digital assets, smart contracts, and compliance requirements. As regulatory frameworks mature, more organizations are expected to move from small pilots to large-scale blockchain deployments with greater confidence.
With so many innovations on the horizon, it’s always tempting to hop on the latest technology. But before you jump into a blockchain initiative, here’s how to evaluate whether it truly aligns with your business goals.
How can you evaluate blockchain feasibility for your business?
Whether you’re in finance, healthcare, real estate, or any other industry, it’s essential to look beyond the hype and assess whether blockchain is the right fit for your organization. Take a close look at how this technology aligns with your goals and challenges. Use this practical checklist to help you make an informed decision:
- Trust gaps: Are you dealing with situations where stakeholders or partners can’t agree on a single version of records, or where you need a tamper-proof system to build confidence?
- Multiple verifiers: Does your process involve several independent parties who must approve transactions or share updates in near real time? For example, supply chain handoffs, insurance claims, or cross-border payments.
- Immutable records: Would having a permanent, auditable history of activity reduce compliance risks or speed up regulatory reporting?
- Automation potential: Could smart contracts enforce rules automatically, such as releasing payments when milestones are met, so you can cut manual steps and errors?
- Transparency requirements: Is it essential to share a transparent view of transactions with customers, regulators, or partners to build trust and improve accountability?
- Resource readiness: Do you have (or plan to secure) the skills, tools, and budget to build, integrate, and maintain a blockchain solution over the long term?
If you can clearly answer “yes” to several of these areas, blockchain may be worth pursuing. Here’s a more structured framework to guide your feasibility assessment:
- Define the problem clearly: Start by describing the exact pain point you want to solve. For example, “We need a trusted, shared ledger to track product movement across suppliers without relying on a central authority.”
- Map stakeholders and governance: Identify who will participate in the network and how it will be governed. Decide who maintains nodes, who has permission to validate transactions, and how disputes will be resolved.
- Compare platforms carefully: Evaluate blockchain platforms like Ethereum (public smart contracts), Hyperledger Fabric (private, permissioned networks), or Corda (financial workflows) based on security, scalability, and ease of integration with your existing systems. Use G2 to compare blockchain platforms, see user ratings, and understand how each performs in real-world scenarios.
- Review compliance and security requirements: Work with legal and security teams to confirm data privacy, regulatory obligations, and controls for handling sensitive information. For example, healthcare organizations must consider HIPAA requirements.
- Start with a pilot: Test your concept with a limited-scope pilot that targets a single workflow or business process. Use clear success metrics, such as transaction speed, error reduction, or cost savings, to measure impact before expanding.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on blockchain applications
What is blockchain used for?
Blockchain has many applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Organizations use it for supply chain tracking, digital identity verification, smart contracts, secure payments, voting systems, intellectual property protection, and more.
What are the top applications of blockchain?
Some of the most impactful applications include:
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum
- Cross-border payments and remittances
- Decentralized finance (DeFi)
- Supply chain transparency
- Electronic health records management
- Voting and governance systems
- Digital identity solutions
- Asset tokenization
What are examples of blockchain in real life?
- IBM Food Trust uses blockchain to trace food products from farm to shelf.
- Estonia has implemented blockchain-based e-governance services.
- De Beers tracks the provenance of diamonds to prevent conflict sourcing.
- Walmart uses blockchain to monitor produce supply chains for safety and freshness.
What industries use blockchain the most?
Industries leading blockchain adoption include:
- Financial services and banking
- Healthcare
- Retail and supply chain
- Real estate
- Energy and utilities
- Government and voting systems
- Media and entertainment
Where is blockchain mostly used?
Blockchain is widely used in:
- Digital payments and asset transfers
- Secure data sharing among multiple stakeholders
- Automating agreements through smart contracts
- Verifying the authenticity of goods and documents
Do any banks use blockchain?
Yes, many banks and financial institutions are piloting or actively using blockchain. JPMorgan developed the JPM Coin for instant payments. Santander, HSBC, and Wells Fargo are exploring blockchain for cross-border transactions, trade finance, and settlement processes.
Is blockchain really safe?
Blockchain is considered highly secure due to its cryptographic design and decentralized structure. However, security also depends on how the network is implemented and maintained. While the blockchain ledger itself is resistant to tampering, applications built on top of it (like smart contracts) can still have vulnerabilities if not properly audited.
What are the disadvantages of blockchain?
Blockchain has limitations, including:
- High energy consumption (in some consensus models)
- Scalability challenges for large volumes of transactions
- Regulatory uncertainty in many regions
- Integration complexity with existing systems
How can businesses start using blockchain?
Most organizations begin by identifying a specific problem, such as supply chain inefficiency or a lack of trust between parties, and testing a small pilot project. Businesses can also explore Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms from providers like IBM, or AWS, to simplify implementation.
Think inside the blocks
Blockchain has immense potential for every industry. From cryptocurrencies to voting systems, blockchain has a broad spectrum of use cases that transform the way we have been functioning for years. It’s like a digital superpower that supports every sector and makes it better than ever by breaking it free from flawed traditional systems.
But perhaps the most important shift isn’t technical. It’s cultural. As blockchain matures, organizations will need to rethink how they share data, collaborate with competitors, and empower customers to take control of their information. This mindset shift could become the true catalyst for innovation.
As artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data continue to converge with blockchain networks, businesses that embrace this transformation early will be best positioned to reimagine how value is created and delivered. The opportunity isn’t just to modernize processes. It’s to build entirely new ecosystems that weren’t possible before.
As you explore new possibilities for blockchain in your organization, don’t overlook the importance of security. Make your blockchain ecosystem immune to cyber threats by using the best blockchain security software.
This article was published in 2023 and has been updated with new information.